Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-29 Origin: Site









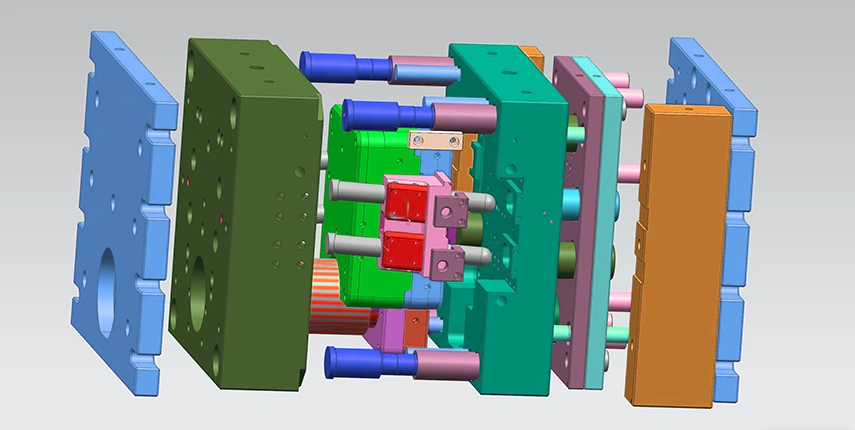
Die-casting molds are the core equipment in die-casting production, with a complex structure and multiple systems working in coordination. Aluminum die-casting molds should be made of steel with high thermal fatigue strength and strong wear resistance, with H13 being the most commonly used. A complete die-casting mold is usually composed of the following core parts:
1. MoldingSystem
CavityInsert: It is embedded in the mold sleeve plate, and its cavity surface determines the external shape of the product.
CoreInsert: Embedded in the coreinsert sleeve plate, its core surface determines the internal shape of the product.
Slider: Used for forming holes or grooves on the side of the product, it can move along the inclined guide direction.
2. MoldBase/Frame System
Fixed mold part: It includes the fixed mold seat plate (for connecting the machine) and the fixed mold sleeve plate (for installing inserts).
Moving mold part: It includes the moving mold sleeve plate (for installing the insert), the moving mold seat plate (for connecting the machine), and the push plate (for installing the ejection mechanism).
Guide components: Guide pin and guide bushing, ensuring precise clamping of the moving and fixed molds.
3. GatingSystem
SprueBushing: The inlet through which molten metal enters the mold from the injection punch of the die-casting machine.
SprueSpreader: Guides the molten metal from the gate sleeve to the runner.
Runner: A channel for transporting molten metal to the inner gate.
Gate: A narrow entrance between the runner and the cavity.
Overflow&Vent: Usually located at the end of the metal flow on the parting surface.
4. Core-pulling System
AnglePin/CamPin: During mold opening, the Angle difference is utilized to drive the slider to complete the lateral core-pulling action.
LockBlock/HeelBlock: After the mold is closed, it locks the slider, withstanding the huge metal pressure during injection to prevent the slider from retreating.
5. EjectionSystem
EjectorPin: The most commonly used ejection component, applied to the parts of the product with greater strength.
ReturnPin: During mold closing, the contact between the moving and fixed molds forces the ejection system to accurately reset.
EjectorPlate: A movable plate for installing and fixing all ejected parts.
6. CoolingSystem
CoolingChannel: Pipes drilled inside the fixed/moving mold inserts, mold bases and sliders, used to circulate cooling water to control the mold temperature.
7. PartingLine (P.L.)
The plane where the moving mold and the fixed mold come into contact with each other is the most important reference surface of the mold.
Brief introduction to the workflow:
1. Mold closing: The moving mold moves towards the fixed mold. The guide pins and guide sleeves are aligned first. Finally, the moving and fixed molds are locked. The inclined guide pins are inserted into the slider, and the locking block locks them in place.
2. Injection: The molten metal fills the cavity at high speed and high pressure through the pressure chamber, gate sleeve, runner and inner gate.
3. Cooling: The molten metal cools and solidifies in the cavity, and the cooling system accelerates this process.
4. Mold opening: The moving mold retracts, and the inclined guide column drives the slider to perform lateral core-pulling. The moving and fixed molds are separated on the parting surface.
5. Ejection: The ejection system of the die-casting machine is driven by the ejection rod of the mold, and the ejection pin pushes the casting off the moving mold.
6. Reset: Before closing the mold, the reset rod touches the fixed mold, pushing the ejection system to accurately reset and prepare for the next cycle